Flow Cytometry and Microbiology

Rapid assessment of cellular viability using flow cytometric assays.
Kuo-Ping Chiu, Diana Davis, Fabio Frezzini and Dwight Kirkpatrick
Bio-Rad Laboratories
Diagnostics Group
4000 Alfred Nobel Drive
Hercules, CA 94547 USA
 email: kuoping_chiu@bio-rad.com
email: kuoping_chiu@bio-rad.com
 email: diana_davis@bio-rad.com
email: diana_davis@bio-rad.com
 email: dwight_kirkpatrick@bio-rad.com
email: dwight_kirkpatrick@bio-rad.com
Data Examples
The following data examples were generated using the Bryte HS flow cytometer with a XeHg arc lamp as the light source.
- Viability determinations using Syber Green I (live) and propidium iodide (dead).
Samples were analyzed using the FITC-520 excitation block and GR1 fluorescence separator block.
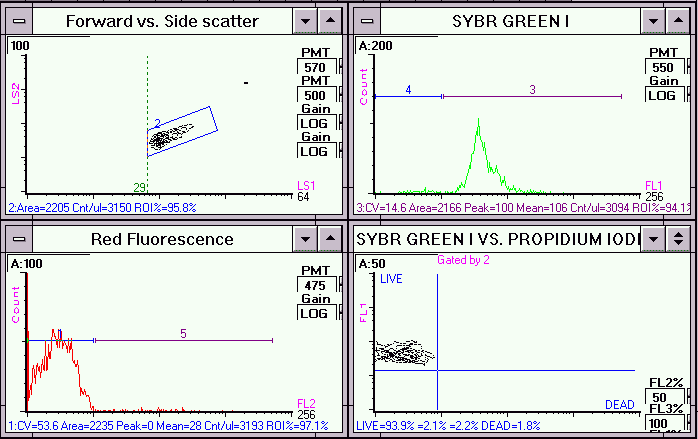
Live Escherichia coli cells stained with Syber Green I and propidium iodide. In the dual parameter plot,
FL2 fluorescence (red) versus FL1 fluorescence (green) of the gated population (region 2), Syber Green I stained the majority of
the cells [live population].

Alcohol fixed (70% ethanol) E.coli cells stained with Syber Green I and propidium iodide. In the dual parameter plot, FL2 fluorescence (red) versus FL1 fluorescence (green) of the gated population (region 2), propidium iodide stained the majority of the cells [dead population].

Unstained E.coli cells. No significant fluorescence in the FL2 versus FL1 dual parameter plot.
- Antibiotic susceptibility studies
- E.coli
Samples were analyzed using the UV-FITC excitation block and the BG1/GR1 fluorescence separator block.

Ampicillin susceptible E.coli strain xb incubated with ampicillin for 15 minutes and stained with a combination of DAPI (live) and Sytox Green (dead).

E.coli strain xb stained with a combination of DAPI (live) and Sytox Green (dead). No antibiotic was added. Control used to establish viability of cells before antibiotic treatment.

Ampicillin resistant E.coli strain pxb incubated with ampicillin for 15 minutes and stained with a combination of DAPI (live) and Sytox Green (dead).

E.coli strain pxb stained with a combination of DAPI (live) and Sytox Green (dead). No antibiotic was added. Control used to establish viability of cells before antibiotic treatment.
- Staphylococcus aureus
Samples were analyzed using the FITC-520 excitation block and the GR1 fluorescence separator block.

Staphylococcus aureus cells treated with an experimental antibiotic for 15 minutes and then stained with DiBAC4(3), a membrane potential dye which enters and binds to the cytoplasmic components of cells whose membrane potential has been perturbed. 3 regions were drawn around different subpopulations of cells on the dual parameter light scatter cytogram (regions 3,5,8). Analysis based on the FL2 fluorescence of the gated populations determined that 80 % of the cells are DEAD and 20 % LIVE.

S. aureus cells stained with DiBAC4(3) (dead). No antibiotic was added. Control used to establish viability of cells before antibiotic treatment.

Unstained S. aureus cells. No antibiotic was added.
- Contaminated Meat
Samples were analyzed using the FITC-520 excitation block and the GR1 fluorescence separator block.

Contaminated meat sample stained with Syber Green I. In the dual parameter plot,
FL2 fluorescence (red) versus FL1 fluorescence (green) of the gated population (region 7), Syber Green I stained the majority of
the cells [live population].
 Back to Flow Cytometry and Microbiology Introductory Page
Back to Flow Cytometry and Microbiology Introductory Page
CD ROM Vol 2 was produced by staff at the Purdue University Cytometry Laboratories
and distributed free of charge as an educational service to the cytometry community.
If you have any comments please direct them to
Dr. J. Paul Robinson, Professor & Director, PUCL, Purdue University, West Lafayette,
IN 47907. Phone:(317) 494-0757; FAX (317) 494-0517; Web http://www.cyto.purdue.edu EMAIL robinson@flowcyt.cyto.purdue.edu




 email: kuoping_chiu@bio-rad.com
email: kuoping_chiu@bio-rad.com email: diana_davis@bio-rad.com
email: diana_davis@bio-rad.com email: dwight_kirkpatrick@bio-rad.com
email: dwight_kirkpatrick@bio-rad.com










 Back to Flow Cytometry and Microbiology Introductory Page
Back to Flow Cytometry and Microbiology Introductory Page