Fluorochrome-conjugated avidin is then used in the last step of the reaction to label DNA strand breaks, thus allowing the visualisation by flow cytometry. The procedure of DNA strand break labelling is rather complex and involves many reagents, but it offers many advantages as compared to other methods (e.g. propidium iodide). First of all the possibility to analyse early apoptotic events, when neither cell morphology changes nor extensive DNA breaks are detectable. It allows to visualise apoptotic cells even when the cell morphology does not show any alteration in light scatter parameters. Furthermore, by combining the TdT assay with cell surface immunophenotyping, it is possible in a single measurement, to identify apoptotic cells in a specific cell subpopulation.
2A.1 Materials
2. After 30 min of incubation on ice in the dark, wash by adding 3 ml of PBS-0.1% BSA and centrifuge at 250xg for 10 min at 4°C.
3. Fix the cells adding dropwise to the pellet 600 ml of pre-chilled (-20°C) 70% ethanol while gently vortexing. Incubate for 30 min at -20°C. The incubation can be performed also for longer periods (up to 24 hours). Centrifuge at 560xg for 5 min at 4°C.
4. Wash the pellet with 3 ml of PBS and centrifuge at 250xg for 10 min at RT.
5. Resuspend the pellet into 90 ml of PBS and add 10 ml of RNAse. Incubate for 30 min at RT in the dark, then add 150 ml of PI.
2A.3. FACS Acquisition and Analysis

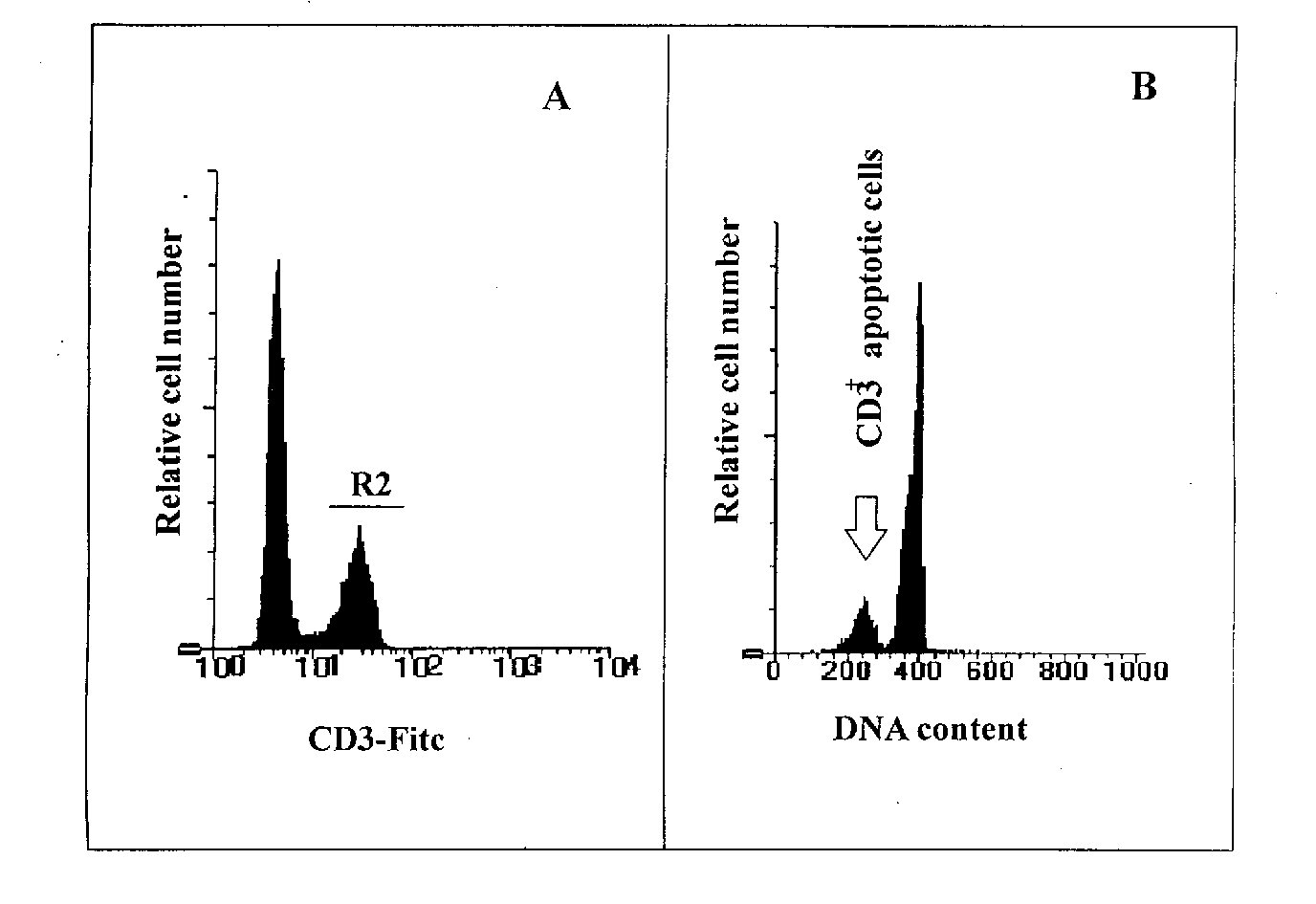
Figure 1: Example of a CD3 surface staining performed together with propidium iodide staining to detect apoptosis occurring in CD3+ T cells of a mouse spleen cells population. A mouse spleen cell population was analysed for apoptosis on CD3+ cells. The events were visualised using simultaneously the forward scatter (FSC) and the side scatter (SSC) parameters. Debris and dead cells were excluded by setting the FSC threshold and, during the analysis of the data, a region was drawn on viable cells (R1). Figure 1A shows the staining of the cells with an anti-CD3 FITC conjugated antibody by standard immunofluorescence techniques. In Figure 1A a region 2 (R2) has been created in the FL1 logarithmic scale on the CD3+ cells, and after combination of R1 (viable cells) and R2 (CD3+ cells) the DNA content analysis was performed in the FL2 linear scale. Figure 1B shows that apoptotic CD3+ cells are visualised as a subdiploid peak due to DNA fragmentation.
2B. Second protocol
2B.1. Materials
1. Stain 106 cells into a FACS tube using a FITC-conjugated monoclonal antibody, performing a routinary surface staining method.
2. After 30 min of incubation on ice in the dark wash by adding 3 ml of PBS-0.1%BSA and centrifuge at 250xg for 10 min at 4°C.
3. Fix the cellular pellet by adding, while gently vortexing, 450 ml of PBS and 150 ml of 4% PFA and incubate for 15 min at RT. Then add 3 ml of PBS-0.1% BSA and centrifuge at 250xg for 10 min.
4. Repeat the fixation adding dropwise to the pellet 600 ml of pre-chilled (-20°C) 70% ethanol while gently vortexing. Incubate for 30 minutes at -20°C. The incubation can be performed also for longer periods (up to 24 hours). Centrifuge at 560xg for 5 min at 4°C.
5. Wash the pellet with 3 ml of PBS-0.1% BSA and centrifuge at 250xg for 10 min at 4°C.
6. Add to the pellet 2 ml of 1x TdT buffer and centrifuge at 250xg for 10 min at 4°C.
7. To perform the TdT reaction, resuspend each sample in 40 ml of TdT buffer containing 100 mg/ml of BSA*, 0.3 nmoles of b-dUTP and 0.1 U/ml of TdT. Incubate for 45 min at 37°C in a water bath .
8. Add 3 ml of PBS-0.1% BSA and centrifuge at 250xg for 10 min at RT.
9. Resuspend the pellet into 90 ml of staining buffer and add 10 ml of SA-PE pre-diluted 1:10 into the staining buffer. Incubate for 30 min at RT in the dark and wash with 3 ml of PBS-0.1% BSA by centrifuging at 250xg for 5 min.
2B.3. FACS Acquisition and Analysis
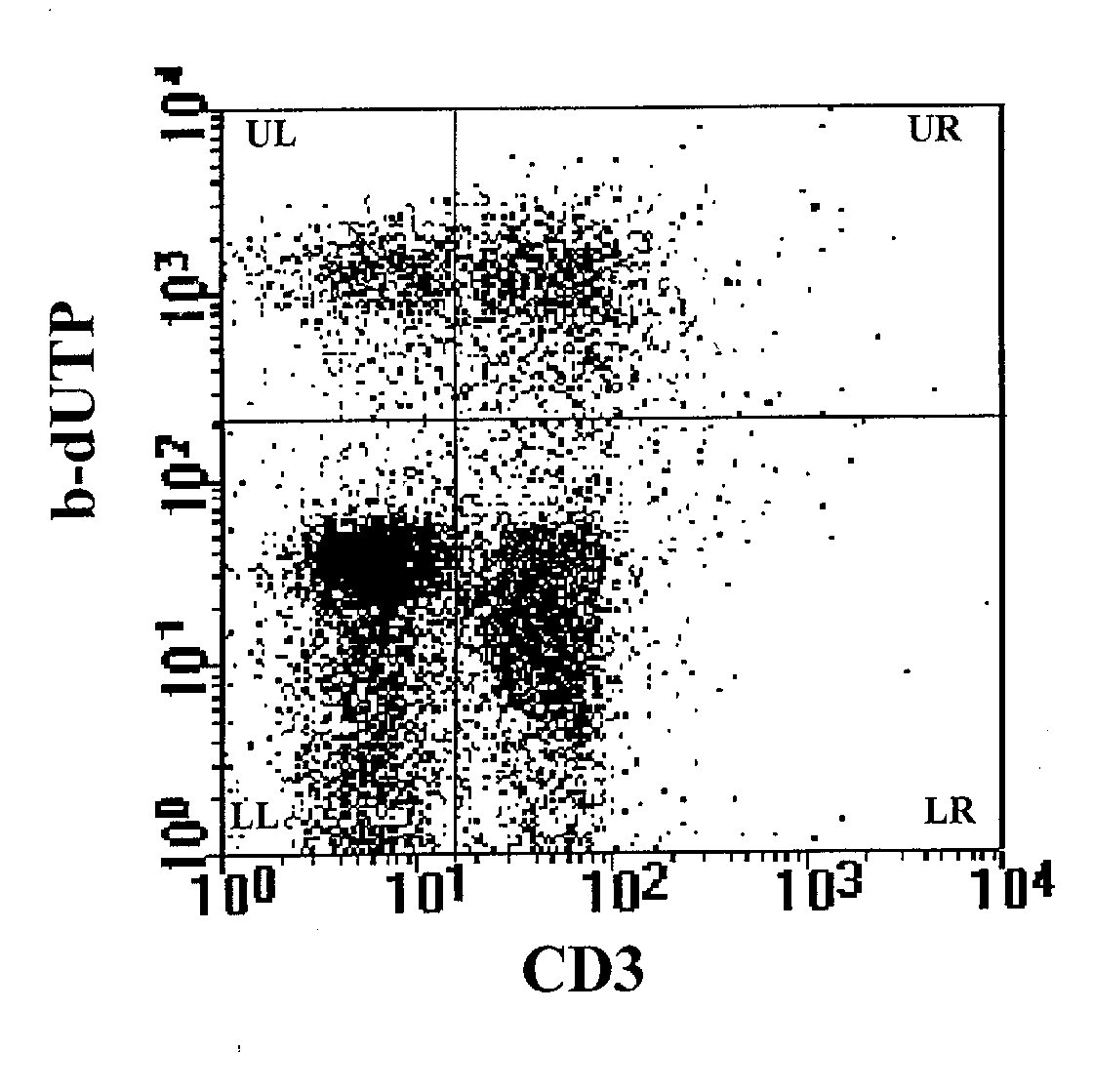
Figure 3: Detection of apoptosis by combining the TdT assay
on cell supension with cell surface immunophenotyping. The analysis, performed
on the cell population represented in R1 region of Figure 2, shows a cell
surface staining with anti-CD3 mAb on FL1, and the labeling of the DNA
breaks with b-dUTP on FL2. The upper right panel (UR) provides simultaneously
data of apoptosis on CD3+ cells, the upper left panel (UL) data of apoptosis
on CD3- cells. The two lower panels (LR and LL) show respectively CD3+
and CD3- non apoptotic cells .
3.1 Troubleshooting
During the methodology it may be possible to lose the cells. It is very
important to use PBS-0.1% BSA for washing, and to follow carefully
the speed and the time of the spinning steps.
2. Nicoletti, I., Migliorati, G., Pagliacci, M. C., Grignani, F. and Riccardi, C 1991. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Meth. 139: 271.
3. Yamada, T. and Ohyama, H. 1988. Radiation-induced interphase death of rat thymocytes is internally programmed (apoptosis). Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 53: 65.
4. Williams, G. T., Smith, C. A., Spooncer, E., Dexter, T. N. and Tylor, D. R. 1990. Haemopoietic colony stimulating factors promote cell survival by suppressing apoptosis. Nature 343: 76.
5. Odaka, C., Kizaki, H. and Tadakuma, T. 1990. TCR-mediated DNA fragmentation and cell death in the T cell hybridoma. J. Immunol.144: 2096.
6. Arends, M. J., Morris, R. G. and Wyllie, H. 1990. Apoptosis: the role of endonuclease. Am. J. Pathol. 136: 593.
7. Swat, W., Ignatowicz, L. and Kisielow, P. 1991. Detection of apoptosis of immature Cd4+8+ thymocytes by flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Meth. 137: 79.
8. Gorczyca, W., Gong, J. and Darzynkiewicz, Z. 1993. Detection of DNA strand breaks in induvidual apoptotic cells by the in situ terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and nick translation assays. Cancer Res. 53: 1945.
Appendix 1 (A1): Stock solutions
|
|
|
|
| Propidium iodide (PI) | Prepare solution of 100 mg/ml PI in PBS or of 50 mg/ml PI in 0.1% sodium citrate plus 0.1% Triton X-100 (2). | Store at 4°C for up to 1 week. |
| Paraformaldehyde 4% in PBS | To prepare 100 ml of fixative:
add 4 g of paraformaldehyde to 50 ml of water. Stir at 65°C on an hot plate (the solution remains slightly cloudy). Add 6 ml of 10 M NaOH. The solution will become clear. Filter trough a paper filter. Add 10 ml of 10x PBS. Adjust the volume to 100 ml with water. |
Store at 4°C for up to 24 hr or store aliquoted at -20°C. |
| 10x TdT buffer | To prepare 1 liter of 10x TdT buffer weigh: 138 gr cacodylic acid (100 mM final), 0.476 g cobalt chloride hexahydrate (0.2 mM final) and 0.154 g 1,4-dithio-DL-threitol (DTT) (0.1 mM final). Fill with distilled water to 1 liter and adjust the pH to 6.8 using NaOH tablets. | Store aliquoted at -20°C. |
| Staining buffer
|
To prepare 0.5 ml, mix: 100 ml 20x SSC, 50 ml Triton X-100 1%, 350 ml distilled H2O. | Sterilize by auto- claving and store at RT. |
| 20x SSC | Dissolve 175.3 g NaCl and 88.2 g sodium citrate in 800 ml of H2O. Adjust the pH to 7.0 with few drops of a 10 N solution of NaOH. Adjust the volume to 1 liter with water. | Sterilize by auto- claving and store at RT. |
Biotin-21-dUTP, 0.5 mmoles/100 µl
5021-1
Clontech
Bovine serum albumin A-9647
Sigma
Bovine serum albumin 711 454
for molecular biology, 20 mg/ml
Boehringer Mannheim
Cacodylic acid C-0125
Sigma
Cobalt chloride C-2644
Sigma
Paraformaldehyde 76240
Fluka
Propidium iodide P-4170
Sigma
RNAse Type I-A R-4875
Sigma
Sodium citrate S-4641
Sigma
Streptavidin-Phycoerythrin, 100 µg/0.4
ml 19539-014
GIBCO BRL
TdT enzyme, 300 U/15 µl M187/1,2
Promega
Triton X-100 T-9284
Sigma
Appendix 3 (A3): Equipment
Centrifuge mod. GS-6R
Beckman
Cytofluorimeter mod. FACScan or Vantage
Becton-Dickinson
Water bath mod. 12B
Julabo